Why measure it?
Inhalation of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) can impair lung function and increase susceptibility to infection, particularly in children. It can also aggravate asthma. NO2 is not only a toxic gas but it is also a precursor to several harmful secondary air pollutants such as ozone and particulate matter. It also plays a role in the formation of acid rain and photochemical smog.
Where does it come from?
Natural Sources
Nitrogen Dioxide is not usually released directly into the air. NO2 forms when nitric oxide (NO) and other nitric oxides (NOx) react with other chemicals in the air. Some NO2 is formed naturally in the atmosphere by lightning and some is produced by plants, soil and water.
As a Pollutant
The major source of nitrogen dioxide in urban environments is the burning of fossil fuels. In urban areas this is most commonly associated with motor vehicle exhaust. Areas with high density road networks close to large populations such as in towns and cities are most at risk of over exposure. Industrial sites will also produce high concentrations of NO2. These include any industry that use combustion processes such as power plants, electric utilities and industrial boilers.
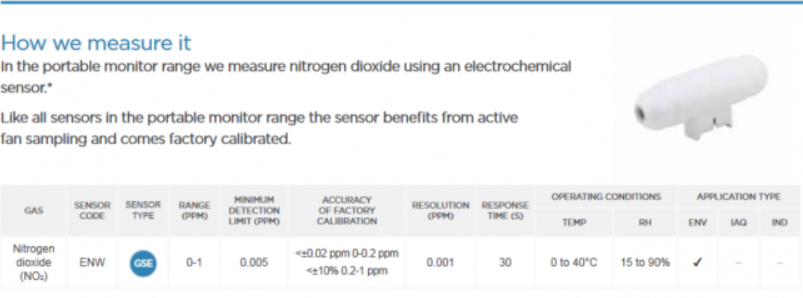
How we measure it
More information on the Aeroqual Gas Detection Monitors can be found on Gas Sensings website, using the links below.


