In the realm of industrial chemicals, peracetic acid occupies a significant position due to its diverse applications in bleaching, disinfection, and laboratory settings. However, its potent nature and associated health risks underscore the importance of proper handling and monitoring. In this blog post, we delve into the characteristics, health risks, regulations, and methods for measuring peracetic acid.
Characteristics of Peracetic Acid
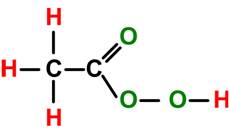
Chemical Formula: C2H4O3; CH3COOOH
Other Names: Peroxyacetic Acid; Ethaneperoxic Acid
CAS Number: 79 – 21 – 0
Industry Uses: Bleaching and Cleaning; Antimicrobial; Chemical Laboratories
Physical Properties:
- Appearance: Colorless liquid
- Odor: Strong, Pungent, Acrid (similar to acetic acid)
- Vapor Pressure: 14.5 mmHg
- Water Solubility: Miscible
- Flammability: Flammable
Health Risks and Exposure
Peracetic acid poses significant health risks if ingested, inhaled, or directly contacted. Even small quantities can lead to severe consequences:
- Ingestion: Causes burning and corrosion of mucous membranes, difficulty swallowing, immediate pain.
- Skin Contact: Results in serious burns, blisters, pain.
- Eye Contact: Causes eye damage.
- Inhalation: Leads to respiratory irritation, labored breathing, sore throat.
Regulations and Exposure Limits
Regulatory agencies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) have established exposure limits for peracetic acid to safeguard human health. These limits include:
- AEGL-1 (8 hrs): 0.17 ppm
- AEGL-2 (8 hrs): 0.52 ppm
- AEGL-3 (8 hrs): 1.3 ppm
Measuring Peracetic Acid
Accurate measurement of peracetic acid concentration is vital for ensuring workplace safety and compliance with regulations. Monitoring can be conducted in air or water (dissolved) using units of parts per million (ppm). Various products, including portable, fixed, and dissolved monitors and kits, are available for this purpose.
All of those units can be found here: https://www.gas-sensing.com/information/peracetic_acid
Conclusion
Peracetic acid, with its potent oxidizing properties and corrosive nature, demands careful handling and monitoring in industrial and laboratory settings. By understanding its characteristics, health risks, regulatory standards, and measurement methods, organizations can effectively mitigate exposure risks and ensure a safe working environment for their employees. Vigilance, adherence to safety protocols, and regular monitoring are essential in harnessing the benefits of peracetic acid while minimizing its potential hazards.