Benzene, a seemingly innocuous chemical compound, hides a sinister secret. While it may be essential in various industrial processes, this colorless liquid is known for its detrimental health risks, with a proven link to cancer and other severe illnesses. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the world of benzene, exploring its properties, industrial applications, health risks, regulations, and the importance of monitoring and detection.
Chemical Nature
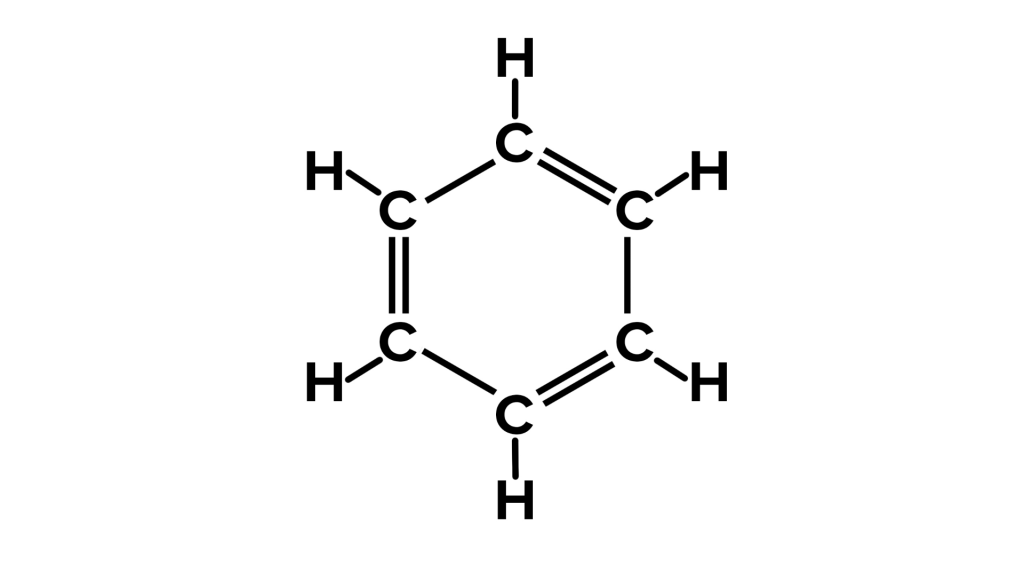
Benzene, with the molecular formula C6H6, is a hydrocarbon. Its structure is unique—a six-carbon atom ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each carbon. This cyclic structure and the continuous pi bonds between carbon atoms classify it as an aromatic hydrocarbon. Benzene is a sweet-smelling, highly flammable liquid, and it’s partly responsible for the distinctive aroma of gasoline. It’s a natural component of petroleum and is used in the production of various chemicals.
Industrial Applications
Benzene plays a crucial role in several industries, including:
- Rubbers: It’s used in the manufacture of synthetic rubbers.
- Lubricants: Benzene is employed in the production of lubricating oils.
- Dyes: It’s a precursor to many dyes and pigments.
- Detergents: Benzene is used to produce detergents.
- Drugs: In pharmaceuticals, it’s a building block for various medications.
- Explosives: It’s used as an essential ingredient in certain explosives.
- Pesticides: Benzene-derived chemicals are utilized in pesticide formulations.
Health Risks
The most alarming aspect of benzene is its health risks. It’s classified as a carcinogen, meaning it significantly increases the risk of cancer. Exposure to benzene is linked to several severe health issues, including:
- Cancer: Benzene is associated with various hematologic malignancies, such as acute myeloid leukemia (AML), aplastic anemia, and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
- Bone Marrow Failure: It’s known to cause bone marrow abnormalities, which can lead to a range of blood-related diseases.
- Cardiovascular Disease: Benzene exposure has also been linked to cardiovascular issues.
Regulations and Exposure Limits
Several regulatory bodies have set exposure limits for benzene:
- AEGL-1 (8 hrs): 0.50 ppm (EPA)
- AEGL-2 (8 hrs): 6.7 ppm (EPA)
- AEGL-3 (8 hrs): 11 ppm (EPA)
- OSHA (8 hrs): 5 ppm (C)
- NIOSH Short Term: 1 ppm
Measuring and Monitoring Benzene
Proper monitoring and detection of benzene are essential to prevent exposure. Monitoring equipment, both portable and fixed, is available to measure benzene concentrations in the air, usually expressed in parts per million (ppm). These devices provide crucial data for environmental assessments and air pollution management.
All out Benzene detectors can be found here: http://Understanding Benzene: A Colorless Chemical with a Dark Side
Conclusion
Benzene is a complex compound with both industrial importance and severe health risks. Its widespread use underscores the importance of stringent safety measures and monitoring to protect workers and the environment. Understanding its properties, applications, and associated health hazards is vital, and taking proactive measures to monitor and limit exposure to benzene is an absolute necessity in various industries.