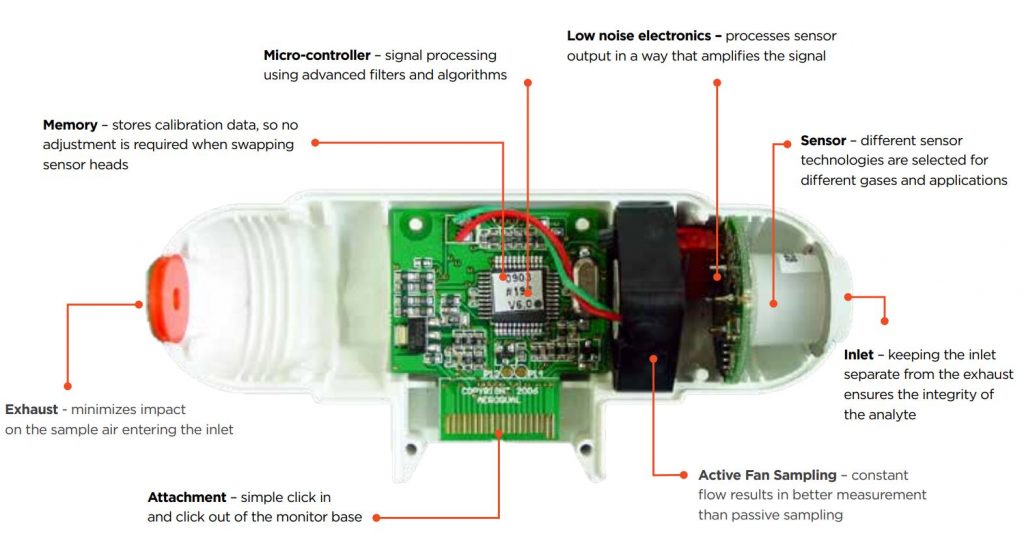
Why measure it?
Methane (CH4) is a non-toxic gas but extremely flammable and can form explosive mixtures with air. Its explosive limits are between 5% (lower explosive limit) and 15% (upper explosive limit) in air. In poorly ventilated areas it is important to ensure the concentration does not exceed safe levels. CH4 displaces oxygen which could lead to asphyxia if leaks occur.
Where does it come from?
Natural Sources
In the environment methane is found underground and below the sea floor where it is slowly released into the atmosphere. It is the main component of natural gas and therefore used as fuel, especially in electricity generation. In many cities it is also piped directly into homes and used for heating and cooking. When released into the atmosphere CH4 is dispersed rapidly as it is lighter than air.
Industrial Sources
The most common source of methane exposure is around landfill sites. CH4 gas is produced naturally via a process called methanogenesis which is a form of anaerobic respiration used by organisms found at landfills. Landfill off-gas can penetrate the interiors of buildings built on or near landfills. Methanogenesis also occurs in ruminants, such as cattle, and therefore CH4 concentrations can also be higher at cattle farms.
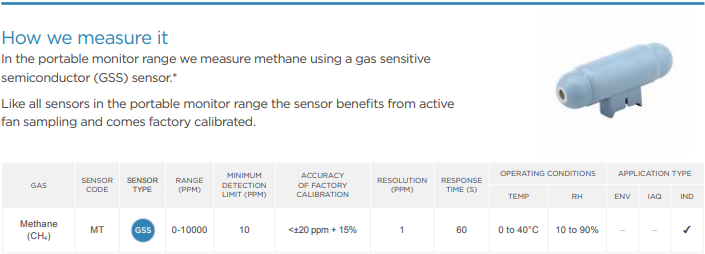
How we measure it
More information on the Aeroqual Gas Detection Monitors can be found on Gas Sensing website, using the links below.