Why measure it?
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are carbon containing gases and vapors such as gasoline fumes and solvents. They evaporate easily at ordinary room temperature which is why they are termed volatile. Many VOCs such as benzene and formaldehyde are highly toxic and can cause cancer and other serious health problems. VOCs such as 1,3 butadiene are also involved in the formation of ground level ozone. The severity of the health effect depends largely on the type of organic compound present as well as exposure time.
Where do they come from?
Natural Sources
The largest source of VOCs is from vegetation however some compounds notably benzene are created during volcanic eruptions and forest fires. Although natural sources of VOC emissions are larger overall, anthropogenic sources are the main contributors of VOCs in urban areas.
As a Pollutant
Anthropogenic sources include fuel production, distribution, and combustion. The largest emissions come from motor vehicles due to either evaporation or incomplete combustion of fuel, and from biomass burning.
Indoor Sources
Typical indoor VOC sources include paint, cleaning supplies, furnishings, glues, permanent markers and printing equipment. Levels can be particularly high when ventilation is limited.
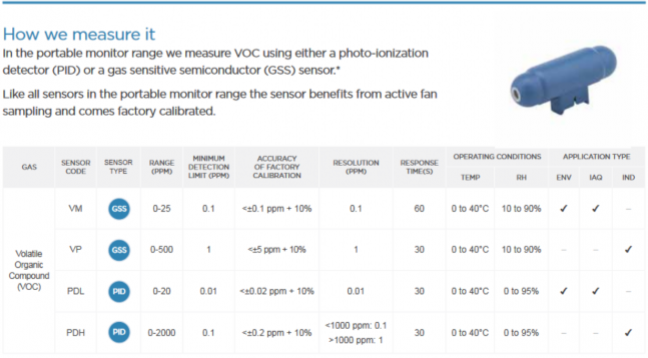
How we measure it
More information on the Aeroqual Gas Detection Monitors can be found on Gas Sensings website, using the links below.

