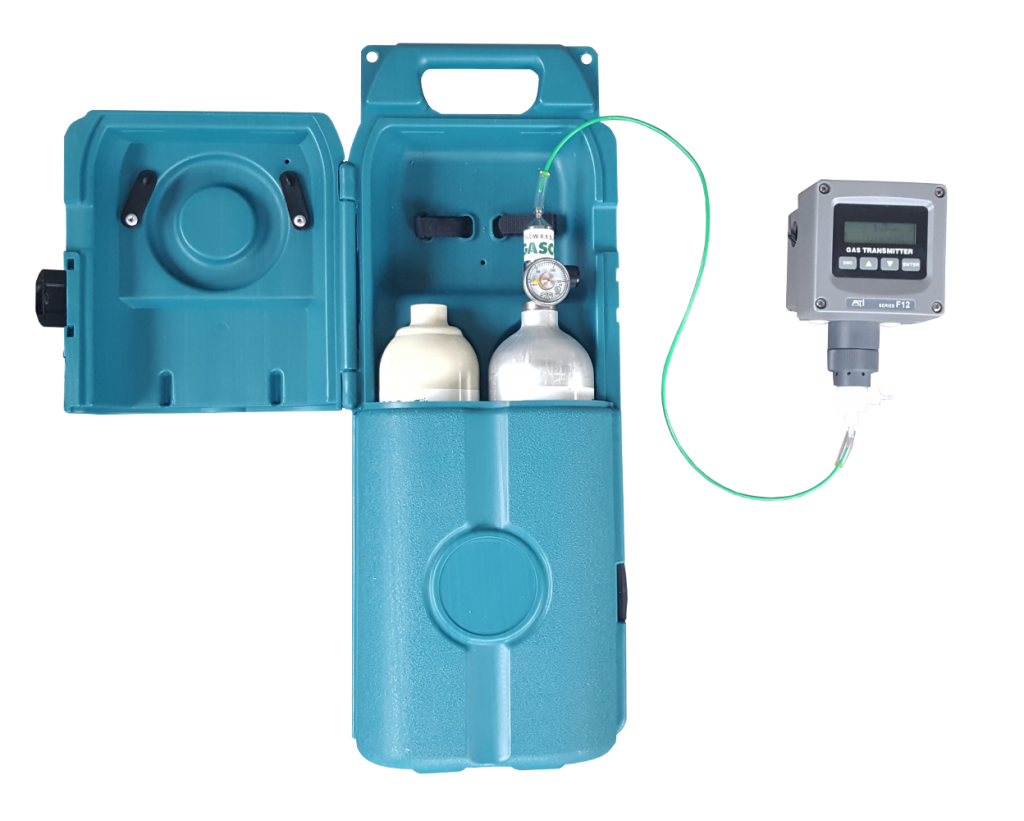
Why measure it?
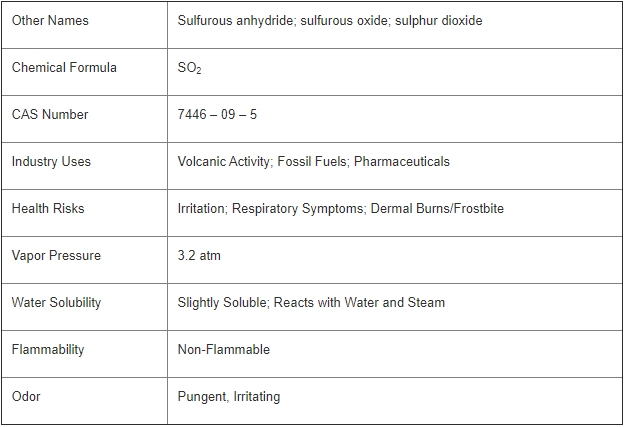
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is a toxic gas with a strong irritating smell. Inhaling sulfur dioxide has been associated with respiratory disease and difficulty breathing. It is also a precursor to acid rain and atmospheric particulate.
Where does it come from?
Natural Sources
Sulfur dioxide is present at very low concentrations in the atmosphere and naturally emitted during volcanic eruptions, as well as at geothermal sites.
As a Pollutant
Fossil fuel combustion at power plants is the largest emission source of SO2 into the atmosphere. Other sources include extracting metal from ore and the burning of high sulfur containing fuels by ships, trains and machinery. Perimeter monitoring at industrial sites is common to measure the concentration of SO2 being emitted into the atmosphere.
Industrial Uses
Sulfur dioxide is an intermediate component in the formation of sulfuric acid. Sulfuric acid is a very important commodity chemical used in several industrial processes including the fertilizer industry and metal treatments. SO2 gas is also used directly in many industries. It acts as a preservative for dried fruits due to its antimicrobial properties and is used in wine making (in the form of sodium bisulfite) to protect the wine from spoilage.
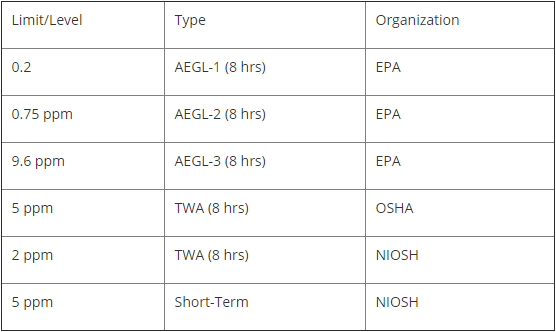
Regulations
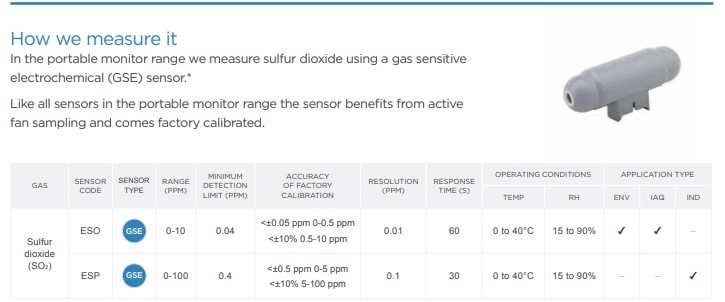
How we measure it
More information on the Aeroqual’s Portable Gas Detection Monitors can be found on Gas Sensing’s website, as well as the links below:


