Chlorine, represented by the chemical symbol Cl2, is a greenish-yellow gas known for its distinctive sharp, bleach-like odor. While it doesn’t exist freely in nature, it is abundant in the form of chloride salts. This blog post aims to provide insights into the various aspects of chlorine, including its properties, uses across different industries, health risks associated with exposure, and the importance of monitoring its levels.
Properties of Chlorine
- Other Names: Bertholite
- Chemical Formula: Cl2
- CAS Number: 7782-50-5
- Vapor Pressure: 6.8 atm
- Water Solubility: Slightly Soluble
- Flammability: Flammable
- Odor: Sharp, Bleach-like
Industry Uses
Chlorine finds its application in various industries, playing a crucial role in:
- Water Purification: Chlorine is widely used to disinfect water, making it safe for consumption.
- Household Cleaners: Its disinfectant properties make chlorine a common ingredient in household cleaning products.
- Pool and Spa Treatments: Chlorine helps maintain water hygiene in swimming pools and spas.
- Pesticides: Some pesticides contain chlorine compounds for effective pest control.
Health Risks of Chlorine Exposure
While chlorine is beneficial in many industrial processes, exposure to this gas poses significant health risks:
- Eye, Throat, and Airway Irritation: Chlorine exposure can cause burns, redness, and irritation.
- Pulmonary Edema, Death: Long-term exposure may lead to severe respiratory conditions, including pulmonary edema, which can be fatal.
- Skin Burns: Direct contact with chlorine can result in skin burns.
- Coughing, Vomiting: Common symptoms of exposure to chlorine gas.
Regulations and Exposure Limits
Regulatory bodies have established exposure limits to ensure the safety of individuals working with or around chlorine:
- 0.50 ppm AEGL-1 (8 hrs)
- 2.8 ppm AEGL-2 (10 min)
- 0.71 ppm AEGL-2 (8 hrs)
- 50 ppm AEGL-3 (10 min)
- 7.1 ppm AEGL-3 (8 hrs)
- 0.5 ppm NIOSH (15 min)
- 1 ppm OSHA Short Term Exposure Limit
- 0.5 ppm OSHA Time-Weighted Average (TWA)
Measuring Chlorine
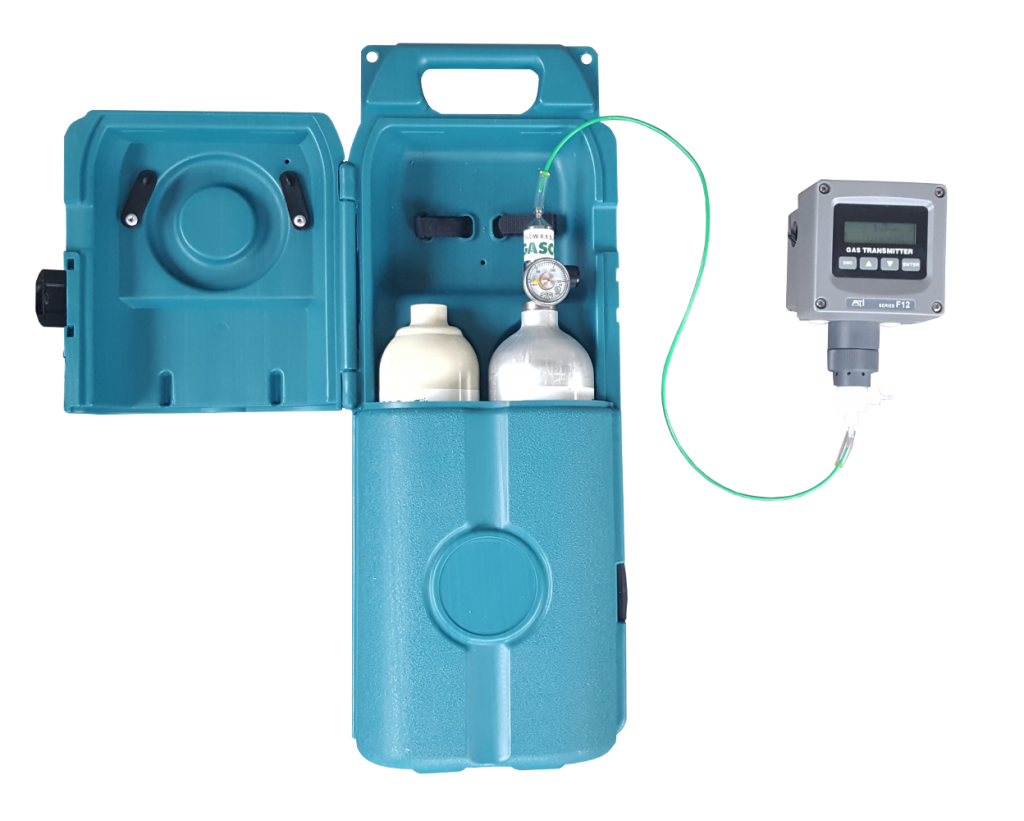
Accurate monitoring of chlorine levels is crucial for ensuring workplace safety and environmental compliance. Chlorine can be measured in the air or dissolved in water, typically reported in parts per million (ppm). Various monitoring tools, including portable, fixed, and dissolved chlorine monitors, are available for different applications. Calibration services are essential to maintain the accuracy of these monitoring devices.
Calibration Services
To ensure the precision of your gas measurements, yearly calibration is recommended. Calibration costs vary based on the type of sensor or monitor:
- Calibration Fee: $150
- Analyzer Calibration Fee: $300
- PM Calibration Sensor Fee: $330
- Genie Calibration Fee: $265
- ATI Calibration Fee: $205
These costs are subject to change based on labor and parts requirements.
Choosing the Right Chlorine Monitor
Selecting the appropriate monitor for your application is crucial. Whether you need a fixed mount, handheld, or dissolved chlorine monitor, our range of products provides options with digital communication capabilities for easy monitoring and control.
For expert guidance on choosing the right monitor or calibration services, feel free to contact us.
In conclusion, while chlorine is a valuable component in various industries, understanding its properties, risks, and the importance of monitoring is vital for maintaining a safe and productive working environment. Regular calibration and adherence to safety regulations are essential steps in ensuring the responsible use of chlorine in industrial processes.