Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) is a colorless, highly toxic gas notorious for its pungent odor of rotten eggs. Widely encountered in various industrial settings, it poses significant health risks and necessitates stringent safety measures. In this blog post, we will delve into the properties of hydrogen sulfide, its health risks, regulatory considerations, and the importance of monitoring its concentration.
Hydrogen Sulfide at a Glance:
- Other Names: Hydrosulfuric Acid; Sulfane; Dihydrogen Monosulfide
- Chemical Formula: H2S
- CAS Number: 7783 – 06 – 4
- Industry Uses: Chemical Laboratories; Metallurgy
- Health Risks: Irritation of eyes and mucous membranes; Convulsions; Headaches, Dizziness
- Vapor Pressure: 17.6 atm
- Water Solubility: Insoluble
- Flammability: Flammable
- Odor: Rotten Eggs
- Hydrogen Sulfide MSDS: Available for comprehensive safety information
What is Hydrogen Sulfide:
Hydrogen Sulfide is a colorless gas with a distinctive rotten egg odor. Highly toxic, it is flammable and naturally occurs in crude petroleum, natural gas, volcanic gas, and hot springs. Known colloquially as “sewer gas,” it is a byproduct of various industrial processes and biogas generators. Its potential to explode when heated under pressure adds another layer of risk. Even more concerning is its ability to deaden the sense of smell quickly, making victims unaware of its presence until it’s too late.
Hydrogen Sulfide Exposure and Health Risks:
Exposure to hydrogen sulfide poses severe health risks. It is not only toxic but also flammable. Inhalation can lead to dizziness, headaches, insomnia, fatigue, and gastrointestinal disturbances. The eyes and respiratory system may experience inflammation, conjunctivitis, and photophobia. Direct contact can result in dermal burns. Prolonged exposure can cause serious damage to organs and the central nervous system, potentially leading to fatalities.
Regulations:
To mitigate the risks associated with hydrogen sulfide exposure, regulatory bodies have established exposure limits. The table below outlines the most recent exposure limits set by organizations such as the EPA, OSHA, and NIOSH:
| Limit/Level | Type | Organization |
|---|---|---|
| 0.33 ppm | AEGL-1 (8 hrs) | EPA |
| 17 ppm | AEGL-2 (8 hrs) | EPA |
| 31 ppm | AEGL-3 (8 hrs) | EPA |
| 20 ppm | C (10 min) | OSHA |
| 10 ppm | C (10 min) | NIOSH |
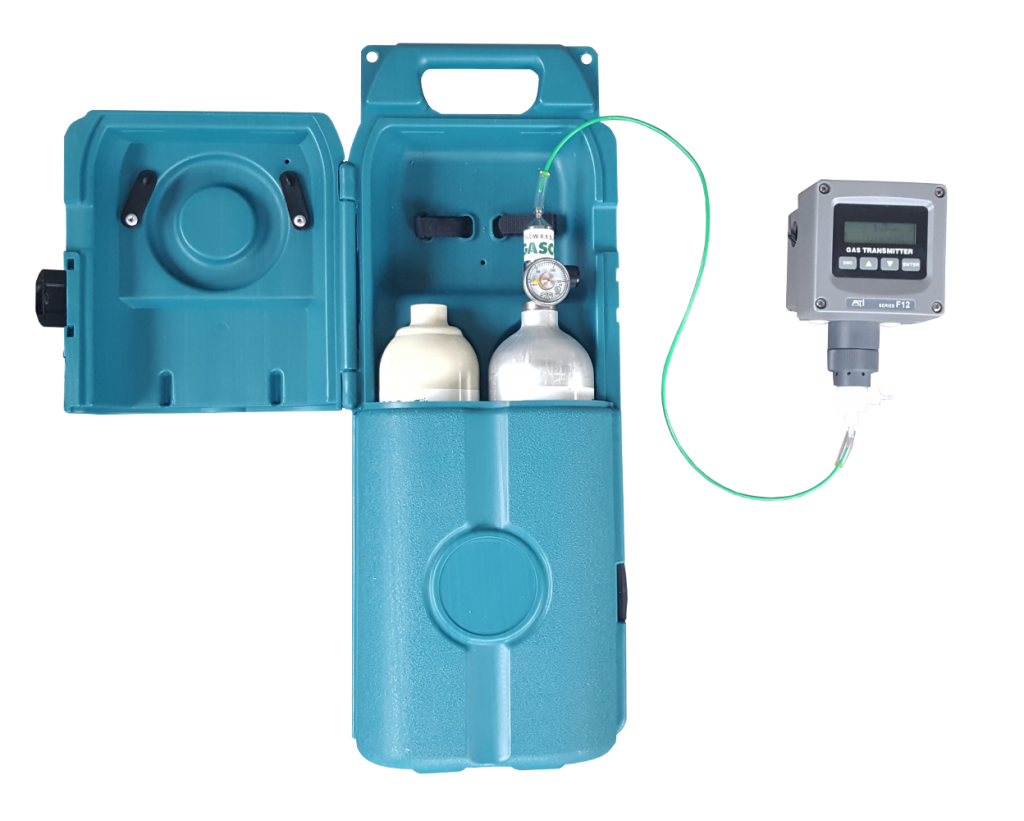
Measuring Hydrogen Sulfide:
All of those units can be found here: https://www.gas-sensing.com/information/hydrogen_sulfide
Monitoring hydrogen sulfide concentration in the air is crucial for ensuring workplace safety. Measurement units typically involve parts per million (ppm). Advanced monitoring solutions, such as portable and fixed hydrogen sulfide monitors and kits, equipped with digital communication capabilities, offer easy monitoring and control. These tools are essential for preventing exposure and maintaining a safe working environment.
Conclusion:
Understanding the properties, risks, and regulatory guidelines associated with hydrogen sulfide is paramount for anyone working in industries where exposure is possible. Implementing robust monitoring solutions is equally crucial. By adhering to safety protocols, utilizing monitoring tools, and staying informed, individuals can significantly reduce the risks posed by hydrogen sulfide, fostering a safer and healthier work environment.