In the realm of chemical compounds, few are as intriguing and paradoxical as nitric oxide (NO). With its diverse roles in both physiological processes and industrial applications, nitric oxide presents a complex interplay between utility and peril. Let’s embark on a journey to uncover the multifaceted nature of nitric oxide, exploring its properties, uses, health risks, and regulatory considerations.
Unveiling Nitric Oxide:
Nitric oxide, a colorless gas with a sharp, sweet odor, belies its deceptive appearance with potent reactivity and biological significance. As an unstable free-radical gas, nitric oxide readily reacts with oxygen to form nitrogen oxides, contributing to its role as both a mediator of cellular communication and a precursor to air pollutants. Produced in mammalian tissues, nitric oxide orchestrates crucial physiological functions such as vasodilation, inflammation modulation, and neurotransmission regulation.
Navigating Health Risks:
Despite its physiological importance, nitric oxide poses significant health risks upon exposure. Inhalation of even small quantities can prove fatal, leading to respiratory irritation, organ damage, and unconsciousness. The rapid onset of symptoms underscores the urgency of mitigating exposure to this toxic gas. Regulatory bodies like the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) have established stringent exposure limits to safeguard workers from the deleterious effects of nitric oxide.
Regulatory Standards:
In accordance with regulatory guidelines, the permissible exposure limits for nitric oxide are set at 25 parts per million (ppm) as a time-weighted average (TWA) over an 8-hour period by both OSHA and NIOSH. These standards serve as crucial benchmarks for ensuring occupational safety and mitigating the risks associated with nitric oxide exposure in industrial settings.
Measuring Nitric Oxide:
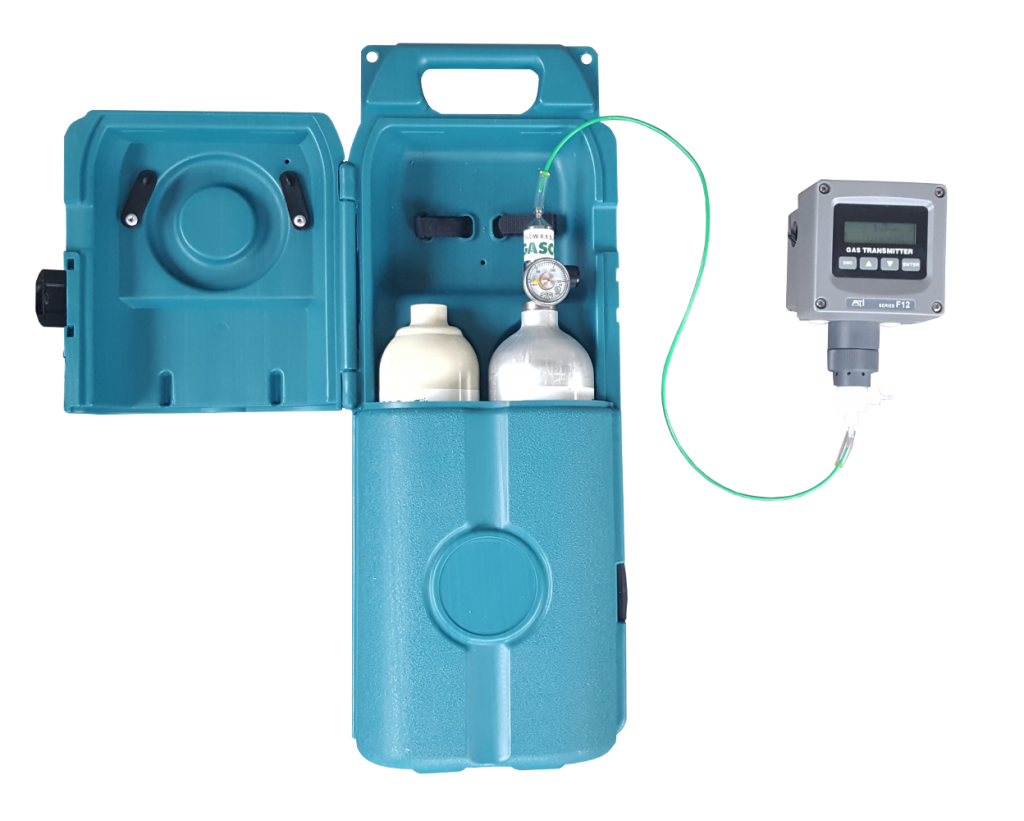
Accurate measurement of nitric oxide concentration in ambient air is essential for assessing workplace safety and implementing effective control measures. Utilizing instruments capable of detecting parts per million (ppm) levels of nitric oxide enables real-time monitoring and timely intervention to prevent exposure-related incidents. A range of portable and fixed nitric oxide monitors and kits are available, equipped with digital communication capabilities for seamless data acquisition and analysis.
All of those units can be found here: https://www.gas-sensing.com/information/nitric_oxide
Conclusion:
Nitric oxide, with its dual identity as a mediator of physiological processes and a potential occupational hazard, epitomizes the intricate relationship between chemistry, biology, and industrial safety. By understanding its properties, health risks, and regulatory considerations, we can navigate the complexities of nitric oxide with greater awareness and diligence. Through adherence to established exposure limits and proactive monitoring strategies, we can harness the benefits of nitric oxide while safeguarding human health and well-being in diverse occupational environments.